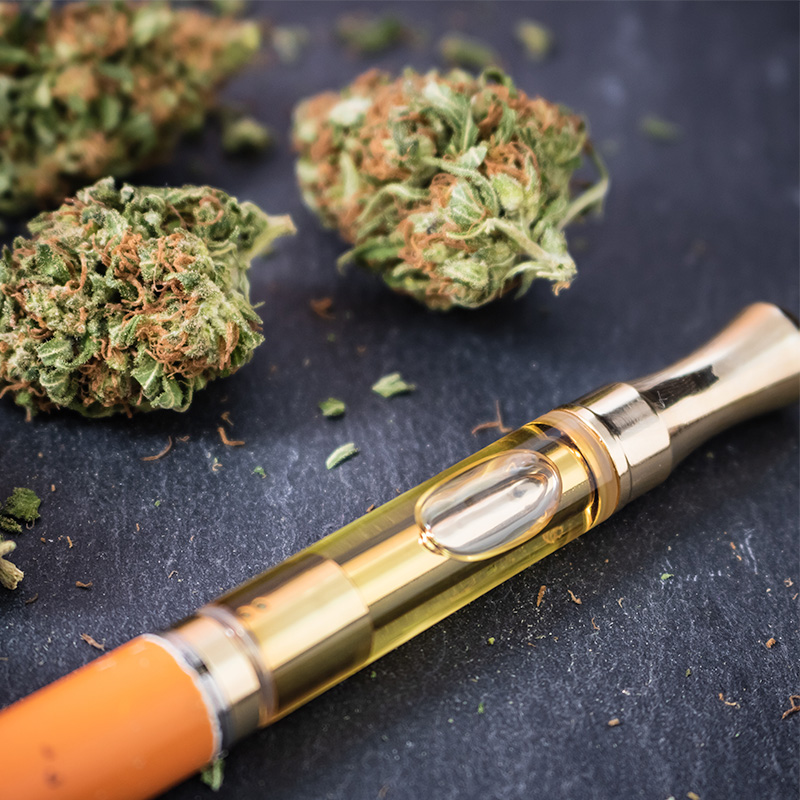

Cannabis Sativa, originating from Southeast and Central Asia, has garnered global attention for its remarkable medicinal and psychoactive potential. Embraced by cultures for centuries, this botanical wonder boasts a rich reservoir of over 500 compounds, including cannabinoids, flavonoids, terpenes, and fatty acids, housed within its leaves and buds. These compounds work synergistically to deliver many health benefits, making Cannabis Sativa a treasure trove of therapeutic promise. [1]

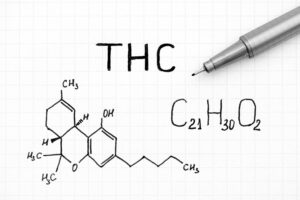
At the forefront of the cannabis revolution stand two phytocannabinoids that command attention - THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol). THC reigns as the principal psychoactive compound, offering euphoric sensations and altering consciousness. On the other hand, CBD offers its own marvels, being non-psychoactive and free from psychotropic effects. This unique combination of phytocannabinoids provides a compelling foundation for diverse medicinal applications.
The captivating allure of Cannabis Sativa does not end with THC and CBD alone. Other phytocannabinoids, such as CBN (Cannabinol), CBG (Cannabigerol), CBC (Cannabichromene), and CBDV (Cannabidivarin), have emerged as subjects of potential pharmacological interest. Though these compounds warrant further investigation, their therapeutic promise holds immense potential for the future of medicine. [2]
Unravelling the chemistry behind THC and CBD reveals a fascinating transformation. They start as acidic precursors, THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) and CBDA (Cannabidiolic Acid), respectively. Through the process of decarboxylation, THC and CBD are born, each offering unique attributes and therapeutic applications. This natural progression contributes to the varying concentrations of these compounds across different cannabis strains and seasons.
Cannabis Sativa's intricate nature also allows it to be classified into three distinct phenotypes based on THC and CBD content. This categorisation helps researchers and enthusiasts alike to comprehend and harness its multifaceted potential.
Historically known for recreational purposes, Cannabis Sativa's trajectory has undergone a paradigm shift, captivating the medical world with its promising therapeutic applications. A growing number of European countries have already embraced its potential, implementing regulations to facilitate research and development. [3]
In recent times, THC vaping has soared to unprecedented heights, captivating cannabis enthusiasts and newcomers alike. This meteoric rise in popularity can be attributed to a perfect blend of factors, including the undeniable convenience and discretion of a THC vape pen, the evolving cannabis culture, and the perception of it being a safer alternative to traditional smoking.
The sheer convenience of THC vaping is a compelling aspect that has won over a vast audience. Vape pens and cartridges offer a discreet and portable method of consuming THC, allowing users to enjoy their favourite strains in diverse settings. Moreover, the absence of the strong smoke odour associated with traditional smoking further adds to its allure, ensuring a more discreet consumption experience without drawing unwarranted attention.
As cannabis gains increasing acceptance and legal recognition in numerous regions, a thriving cannabis culture has blossomed, with vaping at its very core. Embraced as a modern and trendy way to indulge in favourite strains, vaping has seamlessly integrated itself into the cannabis experience for enthusiasts worldwide.
The ever-growing popularity of THC vaping is a testament to its transformative impact on the cannabis landscape, not to mention that there are so many types of THC now available. As this trend continues to captivate both seasoned aficionados and newcomers, the future of THC vaping seems brighter than ever before, promising a convenient, discreet, and enjoyable way to savour the many delights of cannabis. [4]
In the United Kingdom, THC and controlled substances fall under the strict purview of the Misuse of Drugs Act. This comprehensive legislation categorises drugs into three distinct classes - Class A, Class B, and Class C - based on their potential for harm and misuse. Notably, THC, the psychoactive compound present in cannabis, is classified as a Class B substance. As such, possession, production, and distribution of THC without proper authorisation are strictly prohibited and carry severe legal consequences.
Furthermore, the UK enforces stringent regulations regarding the THC content in hemp products. Governed by the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001, industrial hemp cultivation is subject to a maximum THC limit of 0.2%. Any hemp-derived product exceeding this threshold is deemed illegal. Businesses and consumers must remain well-informed about these laws to ensure compliance and avoid the serious legal ramifications associated with non-compliance.
By staying abreast of the Misuse of Drugs Act and the 0.2% THC limit, individuals and businesses can confidently navigate the landscape of THC and hemp-related activities within the UK. Complying with these regulations not only ensures adherence to the law but also upholds the integrity of the cannabis industry while promoting a safer and more responsible approach to the use of controlled substances. [5]

Welcome to an insightful journey into the realm of THC and THC vaping, with a special focus on the legal landscape in the United Kingdom. In this article, we aim to explore diverse facets of THC, shedding light on its intricacies while delving into the laws that govern its use in the UK.
Our mission is to provide you with clear and accurate information, offering a well-rounded perspective on this captivating subject. We will delve into the essential insights of the Misuse of Drugs Act and the 0.2% THC limit on hemp, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of the regulations in place. Whether you're a vaping enthusiast, a seasoned industry professional, or simply curious to learn more about THC and its legal implications, this article is tailored to address your inquiries and deepen your knowledge on the topic.
So, let's embark on this exciting adventure together, exploring the world of THC oil and THC vaping while discovering the boundless potential that lies ahead in this ever-evolving field. Prepare to be enlightened and empowered as we navigate the depths of THC's fascinating domain. [5]
THC vape, also known as THC vaping or cannabis vaping, has become a popular way to consume cannabis in recent times. Unlike traditional smoking, THC vaping uses specialised devices to vaporise active compounds, mainly THC, found in cannabis extracts or oils. This method offers a discreet and convenient way to experience THC's effects without the strong odour of smoking. [6]
To facilitate THC vaping, specific devices with three main components are used: batteries, cartridges, and heating elements. Batteries provide the power to heat the heating element, while cartridges contain the cannabis extract or oil to be vaporised. The heating element, usually a coil or ceramic element, heats the cannabis extract until it turns into an inhalable vapour. Understanding these components is essential for a satisfying THC vaping experience.

THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are prominent cannabinoids found in cannabis, each offering unique effects and potential therapeutic benefits. While THC is known for its psychoactive properties, resulting in the sensation of being "high," CBD does not cause intoxication. Instead, CBD is believed to offer a range of potential therapeutic advantages, including pain relief, anti-inflammatory effects, and stress reduction, without any psychoactive impact. In this guide, we will explore the distinctions between THC and CBD, diving into their various effects and therapeutic potentials, providing valuable insights for those interested in cannabis-based products and making well-informed decisions.
It's essential to understand that full spectrum CBD products, derived from hemp, contain not only CBD but also trace amounts of THC, usually within the legal limit of 0.2% in many regions. These products offer a unique advantage by utilising the entourage effect, where the combination of multiple cannabinoids and compounds enhances their overall effectiveness. Discover the differences between THC and CBD vapes to choose the most suitable option for your needs while staying within legal boundaries. [4,7]

The human body's endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a vital role in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, and immune responses. We will explore how THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) interacts with the ECS, specifically targeting the CB1 and CB2 receptors. These receptors are essential components of the ECS and are distributed throughout the body, with CB1 receptors mainly concentrated in the brain and central nervous system, and CB2 receptors primarily found in peripheral organs and immune cells. We will delve into the intricate mechanisms of how THC binds to these receptors, triggering a cascade of effects that influence mood, cognition, and physical sensations. [8]
The interaction between THC and CB1 receptors in the brain is responsible for the well-known psychoactive effects of cannabis. When THC binds to these receptors, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, altering communication between brain cells and resulting in various cognitive and behavioural changes. Users may experience euphoria, altered perception of time, heightened senses, and modified thought patterns. However, these effects can also lead to short-term memory impairment and impaired motor coordination. [9]
Vaping is a popular method of consuming THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis, by inhaling vaporise cannabis extracts or concentrates. When comparing vaping to other THC consumption methods, such as smoking, edibles, or tinctures, significant differences emerge in terms of onset time and overall effects.
Onset Time: Vaping is renowned for its rapid onset of effects compared to other methods. When THC is inhaled through vaping, it quickly enters the bloodstream via the lungs and crosses the blood-brain barrier, leading to almost immediate effects. This swift delivery makes vaping an appealing choice for individuals seeking rapid relief from pain, anxiety, or other symptoms. [10]
Smoking: Similar to vaping, smoking cannabis provides fast-acting effects as THC is rapidly absorbed through the lungs. However, vaping is generally considered a safer alternative to smoking, as it produces vapour instead of smoke, reducing exposure to harmful toxins associated with combustion.
Edibles: Consuming THC through edibles involves ingesting cannabis-infused products, leading to a slower onset of effects. It can take from 30 minutes to 2 hours for THC to be absorbed through the digestive system and undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver before the effects are felt.
Tinctures: THC tinctures, taken sublingually, also offer a slower onset compared to vaping. While sublingual absorption is faster than edibles, it remains generally slower than vaping, as THC must first be absorbed through the mucous membranes in the mouth before reaching the bloodstream.
First-Pass Metabolism: THC consumed orally, such as through edibles or tinctures, undergoes first-pass metabolism in the liver. This process partially metabolises THC into inactive compounds, reducing its bioavailability and overall potency. In contrast, vaping bypasses first-pass metabolism, allowing inhaled THC to directly enter the bloodstream and reach the brain and target tissues rapidly without extensive liver metabolism. Consequently, the bioavailability of THC through vaping is higher than oral consumption methods.
Higher bioavailability means that a larger proportion of the consumed THC reaches its intended targets, resulting in more potent effects with smaller doses. However, it's essential to note that higher bioavailability also comes with increased potential risks, as rapid and potent effects may increase the likelihood of adverse reactions or overconsumption.
Despite the advantages of vaping in terms of rapid onset and higher bioavailability, safety and responsible consumption practices should be prioritised. Overuse of THC-containing products can lead to negative side effects and potential health risks, especially for individuals with a history of substance abuse or underlying health conditions. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using THC or any cannabis-derived products for therapeutic purposes. [11]
As the popularity of THC vaping continues to rise, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with this method of cannabis consumption. While vaping is often seen as a safer alternative to smoking, it is not without concerns. In this article, we will explore the possible health risks and side effects of THC vaping, shedding light on crucial aspects every user should understand.

By understanding these potential health risks and side effects, users can make informed decisions about THC vaping and take necessary precautions to protect their well-being. Always ensure the use of regulated and reputable products, and consider consulting a healthcare professional for personalised advice on cannabis consumption. [12]
With all that said, it is worth noticing that legally sold full spectrum vapes on our platform contain THC in a very minute and permissible amount. Such a small amount is not known to cause euphoria or other side effects characteristic of high THC products. However, even in minute amounts, THC can contribute to an entourage effect resulting in a better product or vaping experience.
In this discussion, we will explore two common side effects associated with THC vaping. It's crucial to be aware of these potential effects to ensure a safe and comfortable experience while consuming THC through vaping or other methods. [13]
Exploring Therapeutic Applications of THC Vaping: Discover the potential therapeutic properties of THC and how vaping it, under proper medical supervision, may provide health benefits for individuals with specific medical conditions. Some of the discussed therapeutic applications include: [14]

The above-mentioned health effects are mainly seen in clinical studies or are characteristic of medical cannabis. And all the above information is just for educational purposes. However, commonly sold vaping products have only tiny and permissible amounts of THC; thus, these effects are not pronounced. Kindly note that we neither recommend, promote or encourage THC use for medical reasons nor make any such claim.
Personalised Guidance and Risk Assessment: It is important to seek advice from healthcare professionals before using THC vape products. This section emphasises the role of healthcare professionals in providing personalised advice, evaluating potential risks, and considering drug interactions to ensure the safest and most effective treatment approach.

Informed Decision-Making: Users need to empower themselves by understanding the potential risks and benefits of THC vaping for medical purposes. This section aims to educate users on essential aspects such as:
Optimising Health Outcomes: responsible use and moderation are key factors in optimising health outcomes when using THC vaping for medical purposes:


In summary, our exploration has illuminated the vital facets of THC vaping and its far-reaching impact on the realm of cannabis. Our investigation spanned a diverse range of subjects, encompassing the conceivable dangers and advantages linked with THC vaping, underscoring the weight of enlightening users and promoting judicious consumption.
Commencing with an incisive panorama of THC vaping, we delved into its extensive vogue and the assortment of product forms accessible, encompassing vape pens and cartridges. Additionally, we probed into critical health considerations associated with THC vaping, underscoring the significance of procuring top-notch products from trustworthy vendors.
Throughout our discourse, the focal point has been on education's pivotal role in nurturing a secure and prudent approach to utilising THC vape commodities. Outfitting consumers with insights into potential hazards and staying attuned to innovations in vaping technology empowers them to make discerning choices for their well-being.
Contemplating the trajectory of THC vaping, we've accentuated the fluidity of the cannabis sector's landscape, teeming with prospects; we can see that the industry has already started to explore compounds such as THC-O and Delta-8 THC which are three times stronger than THC. Anticipated technological strides are poised to introduce enhanced flavour profiles, potency, and user involvement in THC vape items. In tandem, it remains paramount to envision potential progressions in vaping technology, potentially yielding more efficient and customisable apparatuses while upholding safety protocols to address health apprehensions.
Furthermore, our contemplation extends to the transformative domain of UK cannabis laws. As worldwide attitudes towards cannabis evolve, the UK might reconsider its stance on legislation and regulatory frameworks. Such legal transformations could wield substantial sway over the availability and reception of THC vape goods within the region.

This article is authored by Dr. Chebli Akli Islam (PharmD PhD)

This article was medically reviewed by Dr Preet Pal Singh Bhinder (PhD). Dr. Preet has a Medical degree and Fellowship. He is a Pharmaceutical expert with 19 years of experience.
Disclaimer: All of our products are not intended to diagnose, treat or cure any disease. It is recommended to check with doctor before starting a new dietary supplement program. All CBD products sold have less than 0.2% THC content and abide by both EU an UK law.